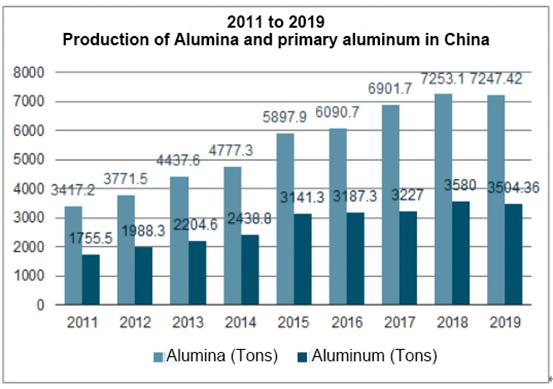
According to the data of "China Aluminum Industry Operation Status and Investment Direction Analysis Report 2020-2026" released by Wise Research Consulting.
China is a major producer and consumer of aluminium, with the world's largest production of alumina and primary aluminium.
China's alumina and primary aluminium production in 2019 was 72.742 million tonnes and 35.043 million tonnes respectively, the production volume is increasing year by year.
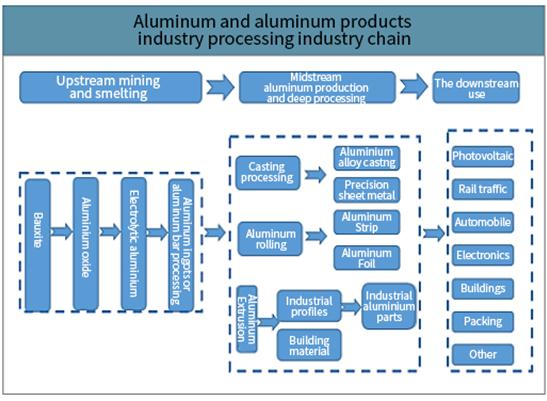
From the industry outlook analysis, aluminium still occupies a huge demand in the market, midstream aluminium production and deep processing are the core of the industry chain.
The main methods of manufacturing aluminium are: casting, rolling, extrusion.
6 series aluminium alloys are hard aluminium alloys with good corrosion resistance, medium strength and excellent hot workability, thus a large number of application in: main grades 6061, 6063 (domestic) ADC12 (Japan).
Applications: 3C products, Home appliances, Automotive, Aerospace, etc.
From the industry market, models such as ADC12, 6063, DM32 and 6061 are no longer able to meet market requirements for the following reasons.
1.ADC12, die-casting aluminium, Nonoxidizing anode, other mechanical parameters: tensile strength: 230MPa, yield strength: 170MPa, post-extension: 1%, hardness 80HBS, rotational bending fatigue strength: 145MPa.
2.6063, alumina, not die-casting, mechanical parameters: tensile strength σb (MPa): ≥ 205, elongation stress σp0.2 (MPa): ≥ 170, elongation δ5 (%): ≥ 7
3.DM32, poor fluidity, die-casting moulds require electroplating or plating factory technology, the parameters of die-casting processing need to adjust, The anode can only spray 120 sand, finer sand will not be able to complete the colouring, low hardness, high temperature of die-casting above 700 ℃, oxidation colour difference.
4.6061, although it can be die-casted and oxidized, but it has a tendency to be warm, tensile strength σb (MPa): 205 MPa or more, yield strength under compression 55.2 MPa, coefficient of elasticity 68.9 GPa, ultimate bending strength 228 MPa
we will explore some of the key aspects of the operation of China's aluminum industry, focusing on the midstream aluminium production as the core of the industry chain. We will address the following four questions:
- What are the main factors that affect the cost and profitability of aluminium production in China?
- How does China's aluminium production compare with other major producers in terms of capacity, output, technology and environmental impact?
- What are the main challenges and opportunities facing China's aluminium industry in the context of global market dynamics and policy developments?
- How can China's aluminium industry improve its competitiveness and sustainability in the long term?
Let's start with the first question: What are the main factors that affect the cost and profitability of aluminium production in China?
The cost and profitability of aluminium production depend on several factors, such as raw material prices, energy costs, labor costs, transportation costs, taxes and fees, exchange rates, and market prices. Among these factors, raw material prices and energy costs are the most significant ones, as they account for about 70% to 80% of the total production cost.
Raw material prices include the prices of alumina, which is refined from bauxite ore, and carbon anodes, which are used in the electrolysis process to produce aluminium. China is the world's largest consumer of alumina, accounting for about 60% of the global demand. However, China has limited domestic bauxite resources, which are of low quality and high impurity. Therefore, China relies heavily on imports of bauxite and alumina from countries such as Australia, Guinea, Indonesia and Brazil. The fluctuations of international bauxite and alumina prices have a direct impact on China's aluminium production cost.
Energy costs include the costs of electricity and natural gas, which are used to power the electrolysis process and the auxiliary facilities. Electricity is the main energy source for aluminium production, accounting for about 40% to 50% of the total production cost. China has abundant coal resources, which are used to generate most of the electricity for aluminium production. However, coal-fired power plants have high carbon emissions and environmental impacts, which may incur higher taxes and fees in the future. Moreover, electricity prices vary across different regions and seasons in China, depending on the supply and demand situation. Therefore, energy costs are also a major factor that affects China's aluminium production cost.
The profitability of aluminium production depends not only on the production cost, but also on the market price. The market price of aluminium is determined by the global supply and demand balance, as well as the speculation and hedging activities in the futures market. China is both the world's largest producer and consumer of aluminium, accounting for about 55% of the global output and 50% of the global demand. Therefore, China's aluminium production and consumption have a significant influence on the global market price. However, China's aluminium market is also affected by external factors, such as trade policies, exchange rates, geopolitical risks and macroeconomic conditions.
In summary, China's aluminium production cost and profitability are influenced by multiple factors, both internal and external. In order to cope with these uncertainties and volatilities, China's aluminium industry needs to improve its efficiency, innovation and resilience.