This article explores the revolutionary technology of additive manufacturing layer by layer, also known as 3D printing. Learn about the process, materials, and applications of additive manufacturing layer by layer and how it is transforming various industries.
Table of Contents:
I. Introduction
- Definition of additive manufacturing layer by layer
- Brief history of additive manufacturing layer by layer
II. How Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer Works
- Step-by-step process of additive manufacturing layer by layer
- Components of additive manufacturing layer by layer machines
- Types of additive manufacturing layer by layer machines
III. Materials Used in Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
- Types of materials used
- Properties of materials
IV. Applications of Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
- Industries that use additive manufacturing layer by layer
- Examples of additive manufacturing layer by layer applications
V. Advantages and Limitations of Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
- Advantages of using additive manufacturing layer by layer
- Limitations of additive manufacturing layer by layer
VI. Future of Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
- Potential advancements in the technology
I. Introduction
Additive manufacturing layer by layer, commonly known as 3D printing, is a revolutionary technology used for creating three-dimensional objects. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which start with a solid block of material and remove material to create a shape, 3D printing adds material layer by layer to create an object. In this article, we will explore how additive manufacturing layer by layer works, the materials used, and its applications across various industries.
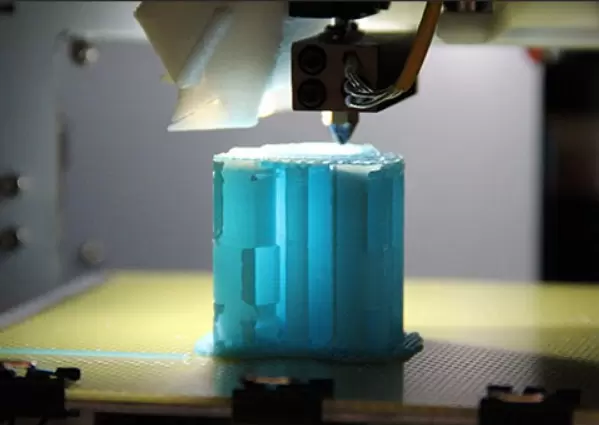
II. How Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer Works
Additive manufacturing layer by layer builds objects by melting or softening material and then depositing it layer-by-layer until the final product is created. The process starts with a 3D model, which is then sliced into thin layers that the 3D printer can understand. The printer then applies each layer of material to the build platform in accordance with the 3D model. The process is repeated layer by layer until the entire object is complete.
Additive manufacturing layer by layer machines consist of several components, including a build platform, extruder, nozzle, and control system. There are various types of additive manufacturing layer by layer machines, ranging from desktop printers to large industrial systems.
III. Materials Used in Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
Additive manufacturing layer by layer can use a wide range of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even food. Some common materials used include PLA, ABS, nylon, and stainless steel. The choice of material will depend on the requirements of the final product, such as its strength, flexibility, and temperature resistance.
IV. Applications of Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
Additive manufacturing layer by layer has applications in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer goods. It is used to create prototypes, tools, and final products such as implants and prosthetics. 3D printing has also been used to create intricate architectural designs and custom fashion pieces.
V. Advantages and Limitations of Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
Additive manufacturing layer by layer offers several advantages, including the ability to create complex geometries, reduce material waste, and shorten production time. However, there are also limitations to consider, such as the quality of the final print and the size of the object that can be printed.
VI. Future of Additive Manufacturing Layer by Layer
As the technology for 3D printing continues to improve, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the future. Advancements in new materials, processes, and equipment are expected to make 3D printing more accessible, faster, and more precise. The future of additive manufacturing layer by layer is an exciting prospect, with everything from large scale production to small form factor applications becoming more and more commonplace.
Additive Manufacturing, also known as 3D printing, has emerged as a revolutionary technology that is transforming the landscape of manufacturing across various industries. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing methods that involve cutting away material from a solid block, additive manufacturing builds objects layer by layer, adding material only where it is needed. This article explores the concept of additive manufacturing layer by layer and the profound impact it has on the manufacturing process and product development.
- The Layer by Layer Approach:
At the core of additive manufacturing lies the layer by layer approach. The process starts with a digital 3D model of the object to be produced, created using computer-aided design (CAD) software. The software then slices the 3D model into thin horizontal layers, generating a set of instructions for the 3D printer to follow. These instructions, known as G-code, guide the printer's movements and material deposition at each layer.
- How Additive Manufacturing Works Layer by Layer:
The additive manufacturing process begins with the selection of suitable printing materials, which can range from polymers, metals, ceramics, to composites. These materials are typically in the form of powders, filaments, or liquid resins.
In the case of powder-based additive manufacturing techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) or Electron Beam Melting (EBM), a thin layer of powdered material is spread evenly across the build platform. A laser or electron beam then selectively melts or sinters the powder, solidifying it into the desired shape for the first layer. The build platform is then lowered, and the process repeats for the subsequent layers until the object is complete.
For filament-based methods like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), a thermoplastic filament is fed through a heated nozzle. The nozzle melts the filament and extrudes it onto the build platform in a predetermined pattern based on the sliced G-code. The platform is then lowered (or the nozzle is raised), and the process continues, layer by layer, until the entire object is fabricated.
- Advantages of the Layer by Layer Approach:
The layer by layer approach in additive manufacturing offers several advantages:
a. Design Flexibility: The ability to build layer upon layer allows for intricate geometries and complex designs that were once challenging or impossible with traditional methods.
b. Reduced Material Waste: Additive manufacturing minimizes material waste as it only uses the necessary amount of material for each layer, reducing overall material consumption.
c. Rapid Prototyping: The layer by layer process enables the rapid production of functional prototypes, allowing for faster design iterations and product development.
d. Customization: Additive manufacturing can create highly customized products tailored to specific needs and requirements.
e. Manufacturing Complexity: It allows for the creation of assemblies with internal structures or moving parts that are manufactured as a single component, reducing the need for assembly and potential points of failure.